Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar, also known as glucose. Whether you’re newly diagnosed, caring for a loved one, or simply looking to stay informed, understanding the relationship between diabetes and blood sugar levels is essential for better health and quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything from the basics of diabetes to tips on managing blood glucose effectively.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a condition where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively. Insulin is a hormone that allows glucose to enter your cells to be used for energy. Without proper insulin function, blood sugar levels can rise dangerously high.
Types of Diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes
Usually diagnosed in children or young adults
The body produces little to no insulin
Requires lifelong insulin therapy
Type 2 Diabetes
More common in adults but rising in children due to obesity
The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough
Often managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, or insulin
Gestational Diabetes
Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after birth
Increases the risk of type 2 diabetes later in life
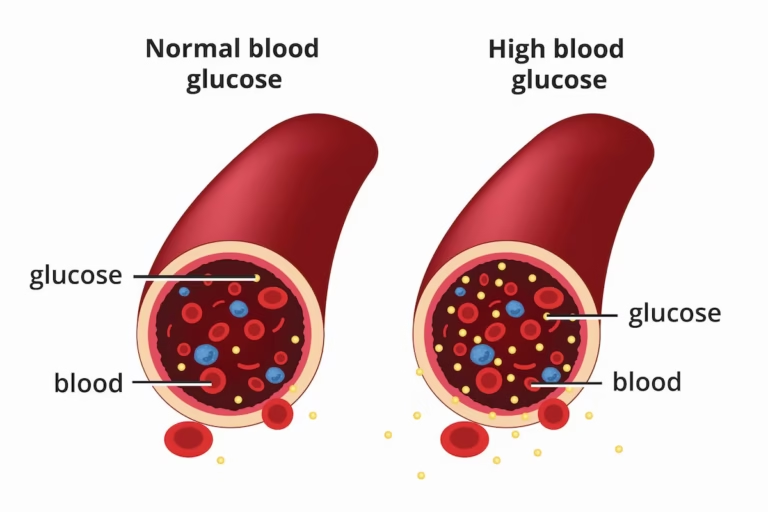
What Is Blood Sugar and Why Does It Matter?
Blood sugar (glucose) is your body’s main source of energy. It’s derived from the food you eat, especially carbohydrates. Blood sugar levels naturally rise and fall throughout the day, but for people with diabetes, these levels can become dangerously high (hyperglycemia) or low (hypoglycemia).
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges:
| Time of Day | Normal Range (Non-Diabetic) | Target Range (Diabetic) |
|---|---|---|
| Fasting | 70–99 mg/dL | 80–130 mg/dL |
| After Meals | <140 mg/dL | <180 mg/dL |
Symptoms of High and Low Blood Sugar
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
Frequent urination
Increased thirst
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Headaches
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Shakiness
Sweating
Dizziness
Confusion
Rapid heartbeat
Why Blood Sugar Control Is Important
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels can help prevent serious complications, including:
Heart disease
Kidney damage
Nerve damage
Eye problems
Stroke
Poor wound healing
How to Manage Blood Sugar Levels Effectively
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are the key components:
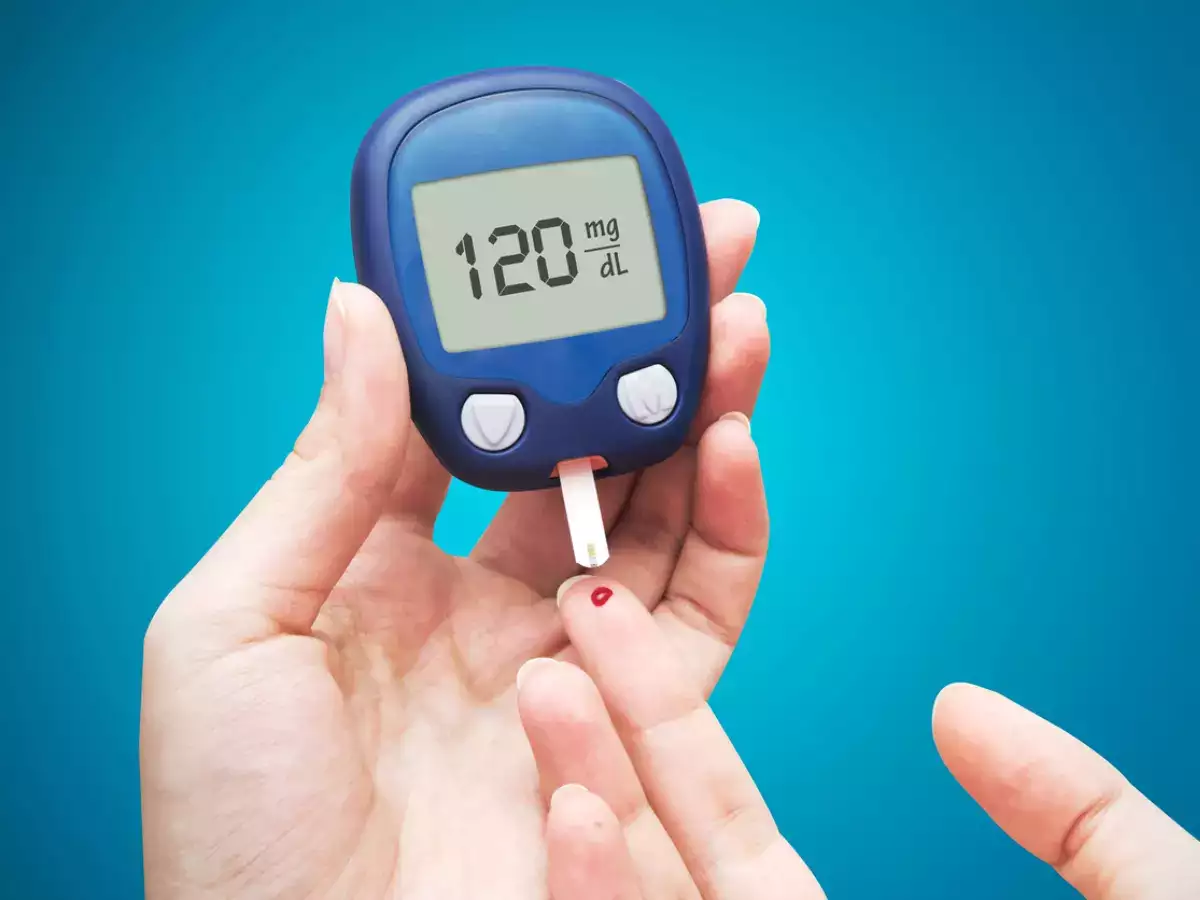
1. Monitor Your Blood Sugar Regularly
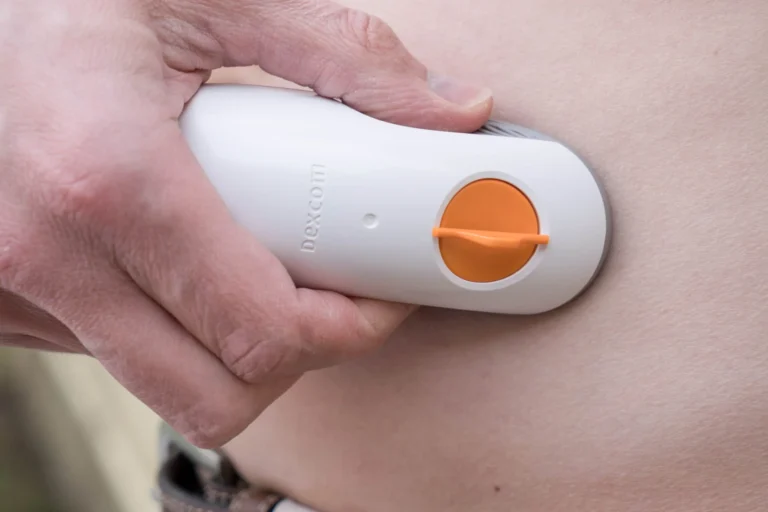
Use a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) like Dexcom
Keep a log of your readings to track patterns
Consult your doctor regularly
2. Eat a Balanced, Low-Glycemic Diet
Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats
Avoid sugary drinks and refined carbs
Practice portion control
3. Exercise Regularly
Aim for at least 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week
Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are great for blood sugar regulation
4. Take Medications as Prescribed
Follow your doctor’s instructions for insulin or oral medications
Never skip doses without consulting a healthcare professional
5. Stay Hydrated and Manage Stress
Drink plenty of water
Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing
Tools That Help: CGMs and Diabetic Supplies
Devices like Dexcom CGMs have revolutionized diabetes care. These tools continuously monitor glucose levels and alert users to highs and lows in real time.
If you have unused Dexcom supplies or extra diabetic strips, consider selling them through a trusted platform like Diabetic Strip Supply. Not only does this help others in need, but it also contributes to diabetes awareness and accessibility.
Need to sell unused diabetic supplies? Call +1 (585) 209-9013 for top cash offers—fast, safe, and reliable.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and managing diabetes and blood sugar levels is crucial to living a healthy, balanced life. Whether you’re dealing with the condition yourself or supporting a loved one, staying informed and proactive can make all the difference.
Make lifestyle changes, use the right tools, and don’t hesitate to seek help from healthcare providers. Every step you take brings you closer to better blood sugar control and improved well-being.